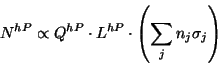
Q: Charge, L: Life-time, nj: number of target nuclei of type j involved,
Measured counts for possible combinations of h and P are given as:
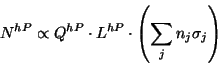
Q: Charge, L: Life-time, nj: number of target nuclei
of type j involved,
![]() :
cross sections. All other factors
like detector acceptance are considered as constant and not dependent on h or
P.
:
cross sections. All other factors
like detector acceptance are considered as constant and not dependent on h or
P.
To keep the expressions for the measured asymmetries as simple as possible it is most favourable to divide the data into sets for which the polarizations can be considered as constant and to normalize each set individually. In the following we call a data set of constant polarization a run.
Assuming that we have m runs with NihP (i=1..m) counts for the different combinations of h and P the normalized sum becomes