


Next: Impact on Physics Asymmetries
Up: E93-026 Technical Note: Electronics
Previous: Electronics dead-time during Gen98
To quantify the helicity dependent asymmetry of the Bar rate Ab we
can use scaler values:
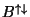 and
and
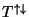 denote the
scaler counts of ``B Pretrigger'' and ``1 MHz Clock'' respectively with
the up arrow indicating the positive helicity2 and the down arrow indicating the negative helicity. Note that this is the
asymmetry of the raw Bar rates not normalized for beam current. According to
the explanation in the previous section it is the raw rate that affects the
electronics dead-time. Ab was calculated for all Q2=0.5runs that made the DEC99 replay. For further insight the beam current asymmetry
was calculated for the same runs too. Fig.
denote the
scaler counts of ``B Pretrigger'' and ``1 MHz Clock'' respectively with
the up arrow indicating the positive helicity2 and the down arrow indicating the negative helicity. Note that this is the
asymmetry of the raw Bar rates not normalized for beam current. According to
the explanation in the previous section it is the raw rate that affects the
electronics dead-time. Ab was calculated for all Q2=0.5runs that made the DEC99 replay. For further insight the beam current asymmetry
was calculated for the same runs too. Fig. ![[*]](/usr/local/latex2html/icons.gif/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows the results
of this study.
shows the results
of this study.
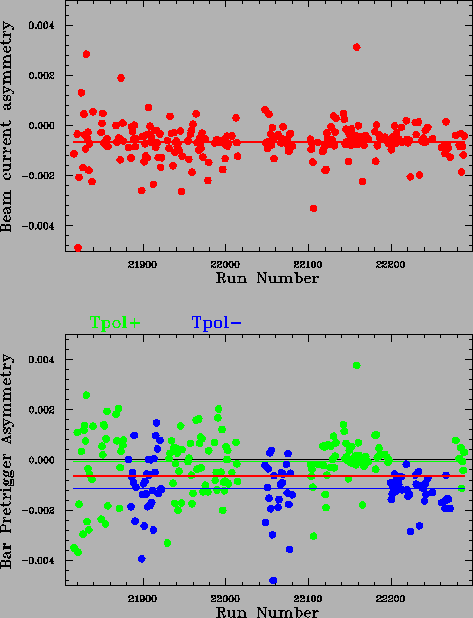
Figure:
The top graph shows beam current asymmetries vs. run number. The two
solid red lines indicate the averages for positive and negative target polarization,
which are basically equal. The bottom graph shows Bar pretrigger rate asymmetries
vs. run number for positive (green) and negative (blue) target polarization.
The two corresponding solid lines indicate the averages and the red line is
again the average of the beam current asymmetry.
|
The average beam current asymmetry is in the order of
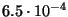 and is the same for both signs of the target polarization as one would expect.
The Bar rate however has an intrinsic asymmetry of the same order as the beam
current asymmetry. This intrinsic asymmetry flips sign with the orientation
of the target polarization. As a consequence we have an asymmetric behavior
behavior with respect to the two signs of the target polarization! The asymmetry
of the raw bar rate is basically 0 for the positive target polarization and
significant for the negative target polarization. The numbers are
and is the same for both signs of the target polarization as one would expect.
The Bar rate however has an intrinsic asymmetry of the same order as the beam
current asymmetry. This intrinsic asymmetry flips sign with the orientation
of the target polarization. As a consequence we have an asymmetric behavior
behavior with respect to the two signs of the target polarization! The asymmetry
of the raw bar rate is basically 0 for the positive target polarization and
significant for the negative target polarization. The numbers are
 for positive and
for positive and
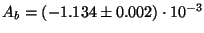 for negative target
polarization.
for negative target
polarization.
Side note 1: The spread in the distribution of bar asymmetries becomes smaller
and is much more correlated with the beam current after run 21000, which is
due to the synchronization of the raster with the helicity.
Side note 2: The intrinsic Bar rate asymmetry has the opposite sign to the coincidence
rate asymmetry and is one order of magnitude smaller.



Next: Impact on Physics Asymmetries
Up: E93-026 Technical Note: Electronics
Previous: Electronics dead-time during Gen98
Marko Zeier
2000-05-04
